Are you considering establishing a prepper’s homestead but don’t know where to start? From planning to execution, this article will guide you through the process step by step. Whether you’re a beginner prepper or looking to enhance your current setup, this comprehensive guide will help you create a sustainable and self-reliant homestead.
Assessing Your Needs and Resources
Before diving into the planning phase, it’s essential to assess your needs and available resources. Consider factors such as location, climate, water supply, and access to essential services. Evaluate your skills, budget, and time commitment to determine the feasibility of your prepper homestead.
Conducting a Self-Assessment
Start by evaluating your skills and knowledge in areas such as gardening, livestock management, and food preservation. Identify any gaps in your skillset and determine how you can acquire the necessary expertise through training or workshops. This self-assessment will help you tailor your prepper homestead to your abilities and interests.
Assessing Your Budget and Resources
Take stock of your financial resources and set a realistic budget for establishing and maintaining your prepper homestead. Consider the costs of purchasing land, building infrastructure, buying supplies, and investing in equipment. Evaluate your available resources, such as tools, seeds, and storage containers, to determine what you already have and what you need to acquire.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting the right location for your prepper homestead is crucial for its long-term success. Factors to consider include climate, soil quality, access to water, and proximity to urban areas. Choose a location that aligns with your goals for self-sufficiency and resilience.
Climate Considerations
Consider the climate of your chosen location and its impact on your ability to grow crops, raise livestock, and maintain a comfortable living environment. Research average temperatures, precipitation levels, and growing seasons to determine if the climate is conducive to your prepper lifestyle. Choose a location with a climate that supports your self-reliant goals.
Soil Quality and Fertility
Assess the soil quality and fertility of potential homestead sites to determine their suitability for gardening and farming. Conduct soil tests to measure nutrient levels, pH balance, and drainage capacity. Choose a location with fertile soil that can support a variety of crops and sustain livestock grazing.
Access to Water
Ensure that your prepper homestead has reliable access to water for irrigation, drinking, and hygiene purposes. Consider sources such as wells, springs, ponds, or rainwater harvesting systems. Evaluate the quality and quantity of water available on the property to meet your needs for self-sufficiency.
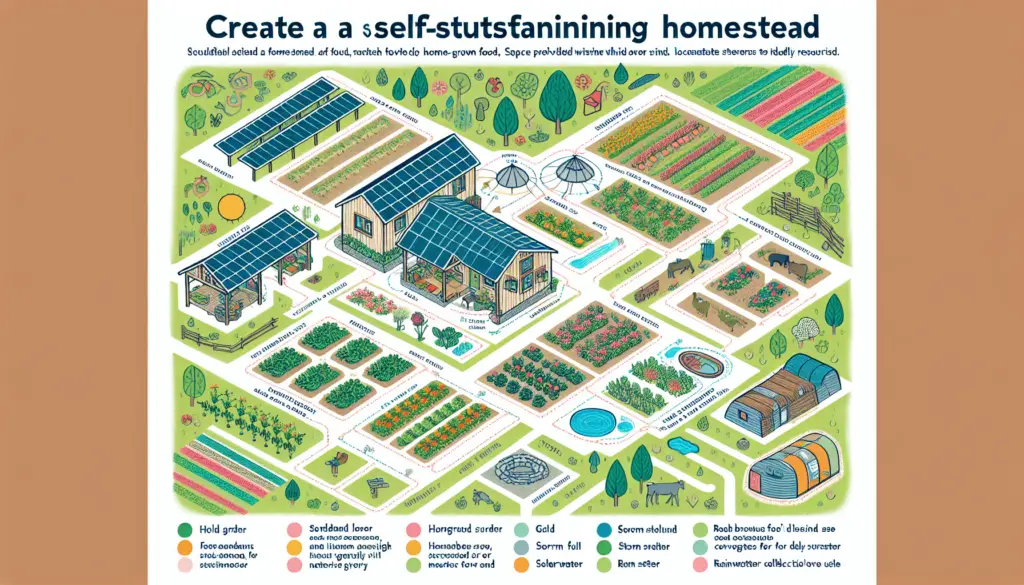
Planning Your Homestead Layout
Once you’ve chosen a location, it’s time to plan the layout of your prepper homestead. Design a functional and efficient layout that maximizes productivity, minimizes waste, and enhances sustainability. Divide your homestead into zones based on use and prioritize key areas such as the garden, livestock pens, and storage facilities.
Designing Zones
Divide your prepper homestead into zones based on their functions to streamline management and optimize productivity. Create zones for gardening, livestock, water storage, food processing, and living quarters. Designate each zone with specific tasks and activities to create a harmonious and organized homestead layout.
Prioritizing Key Areas
Identify key areas of your prepper homestead that require special attention and resources to ensure their success. Prioritize zones such as the garden for growing fruits and vegetables, the livestock pens for raising animals, and the storage facilities for preserving food and supplies. Allocate resources and time to these key areas to establish a strong foundation for your homestead.
Building Infrastructure and Facilities
Establishing a prepper homestead requires building essential infrastructure and facilities to support your self-sufficient lifestyle. Invest in infrastructure such as water systems, power sources, shelter, and storage to meet your basic needs. Choose sustainable building materials and energy-efficient designs to reduce your environmental impact.
Water Systems
Develop a reliable water system for your prepper homestead to ensure access to clean water for drinking, irrigation, and sanitation. Install wells, cisterns, or rainwater harvesting systems to capture and store water on-site. Consider implementing water-saving techniques such as drip irrigation and greywater recycling to maximize efficiency.
Power Sources
Explore alternative power sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric systems to generate electricity for your prepper homestead. Evaluate your energy needs and available resources to determine the most suitable power source for your location. Invest in energy-efficient appliances and lighting to reduce your reliance on grid electricity.

Cultivating a Productive Garden
Growing your fruits and vegetables is a fundamental aspect of a prepper homestead. Cultivate a productive garden to provide fresh produce for your family, enhance self-sufficiency, and promote food security. Implement organic gardening practices, companion planting, and crop rotation to maximize yield and minimize pests.
Soil Preparation
Prepare the soil for planting by tilling, amending, and mulching to create a nutrient-rich and well-draining growing environment. Conduct soil tests to assess nutrient levels and pH balance and adjust as needed to optimize plant growth. Incorporate compost, manure, and organic matter to improve soil structure and fertility.
Plant Selection
Choose a variety of fruits, vegetables, herbs, and flowers to diversify your garden and increase resilience to pests and diseases. Select plants that are well-suited to your climate, soil type, and growing conditions to ensure successful growth. Include heirloom and open-pollinated varieties for seed-saving and long-term sustainability.
Maintenance and Care
Maintain your garden by watering, weeding, fertilizing, and pest control to promote healthy plant growth and maximize yield. Implement sustainable gardening practices such as mulching, crop rotation, and companion planting to improve soil health and reduce reliance on chemical inputs. Monitor plant health and address any issues promptly to prevent crop loss.
Raising Livestock for Sustainability
Keeping livestock is an integral part of a prepper homestead as it provides a renewable source of food, fiber, and manure. Raise animals such as chickens, goats, rabbits, or bees to enhance self-sufficiency, produce nutrient-rich products, and promote biodiversity. Follow ethical and sustainable animal husbandry practices to ensure the welfare of your animals.
Choosing Livestock
Select livestock breeds that are well-suited to your climate, space, and resources to thrive on your prepper homestead. Consider factors such as feed requirements, housing needs, and product yield when choosing animals. Raise a mix of animals such as egg-laying hens, dairy goats, or meat rabbits to meet your diverse needs for protein, dairy, and fiber.
Providing Shelter and Care
Build suitable shelters and enclosures for your livestock to protect them from predators, harsh weather, and disease. Design comfortable and secure housing for animals such as coops, barns, hutches, or hives based on their specific requirements. Provide access to fresh water, nutritious feed, and veterinary care to ensure the well-being of your animals.
Managing Grazing and Foraging
Allow livestock to graze on pasture, forage in orchards, or browse in woodlands to fulfill their natural behaviors and nutritional needs. Rotate animals on grazing areas to prevent overgrazing, soil compaction, and parasite buildup. Supplement grazing with hay, grains, and minerals to ensure a balanced diet and optimal health for your livestock.
Harvesting and Preserving Food
Harvesting and preserving food is essential for maintaining a year-round food supply on your prepper homestead. Implement food preservation techniques such as canning, drying, fermenting, and freezing to extend the shelf life of fresh produce and minimize food waste. Stockpile an ample supply of preserved foods to prepare for emergencies and seasonal shortages.
Canning and Pickling
Preserve fruits, vegetables, and meats through canning and pickling to seal in freshness and flavor. Use water bath canning or pressure canning methods to safely store foods in airtight jars for long-term storage. Pickle vegetables in vinegar brine or ferment them with salt to create tangy and probiotic-rich snacks.
Drying and Dehydrating
Dry herbs, fruits, vegetables, and meats using dehydrators, ovens, or solar drying methods to remove moisture and prevent spoilage. Store dried foods in airtight containers or vacuum-sealed bags to maintain their quality and nutritional value. Use dried ingredients in soups, stews, trail mixes, and snacks for a convenient and shelf-stable food supply.
Fermenting and Fermenting
Ferment fruits, vegetables, dairy, and grains to preserve them while enhancing their taste, texture, and nutritional content. Use lactic acid fermentation or wild yeast fermentation to create probiotic-rich foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, yogurt, and sourdough bread. Fermenting foods increases their shelf life and enhances their digestibility and flavor profile.
Securing Your Homestead
Securing your prepper homestead is essential for protecting your family, property, and resources from external threats and emergencies. Implement security measures such as perimeter fencing, surveillance cameras, guard animals, and emergency drills to deter intruders and respond to threats effectively. Develop a comprehensive safety plan to safeguard your homestead and ensure the well-being of your loved ones.
Perimeter Security
Install perimeter fencing, gates, and alarms to secure the boundaries of your prepper homestead and prevent unauthorized access. Choose durable and high-quality fencing materials such as chain link, electric wire, or wooden panels to deter intruders. Monitor entry points and establish checkpoints to control access and monitor traffic on the property.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Set up surveillance cameras, motion sensors, and security lights to monitor activity around your prepper homestead and alert you to potential threats. Position cameras at key locations such as entryways, storage areas, and livestock pens to capture suspicious behavior. Use monitoring systems connected to alarms or smartphones for real-time notifications and response.
Emergency Preparedness
Create an emergency preparedness plan that outlines procedures for responding to natural disasters, power outages, medical emergencies, and security threats. Develop evacuation routes, assemble emergency kits, and conduct regular drills to practice emergency response protocols. Educate your family members on safety measures and communication methods to ensure a coordinated and swift response in times of crisis.
Conclusion
Establishing a prepper’s homestead requires careful planning, resource management, and commitment to self-sufficiency. By assessing your needs, choosing the right location, planning your homestead layout, building essential infrastructure, and implementing sustainable practices, you can create a resilient and productive homestead. Cultivate a diverse garden, raise livestock ethically, harvest and preserve food, and secure your property to ensure the sustainability and security of your prepper lifestyle. Embrace the journey of self-reliance and preparedness as you establish a prepper’s homestead from planning to execution.
